Symptomatic Central Nervous System Tuberculomas After Completition of Tuberculosis Treatment in an Immunocompetent Adult: A Case Report
Dan Iulian Cuciureanu, Cristina Bîrzu, Cornelia Tudorache, Florentina Danciu, Irina Moisei Constantinescu
Med Sci Case Rep 2016; 3:72-76
DOI: 10.12659/MSCR.900276
Available online: 2016-09-21
Published: 2016-09-21
BACKGROUND:
Granulomatous basal meningitis is an uncommon manifestation of intracranial tuberculosis. Paradoxical reactions consisting of manifestation of or worsening of brain tuberculomas may arise during the proper treatment of tuberculosis. There are a few described cases of cerebral tuberculosis recrudescence after adequate completion of treatment and favorable outcomes.
CASE REPORT:
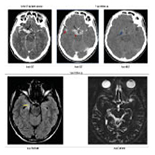
We report the case of a 25 year-old male, immunocompetent, previously diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis and tuberculous meningitis and who underwent anti-tuberculous treatment for one year. The brain imagery performed at the time of the initial diagnosis revealed no intracerebral tuberculous lesions. Six months after the tuberculostatic treatment was stopped, the patient presented with a first epileptic seizure. A neurologic examination showed anisocoria. The cerebral CT scan with contrast enhancement revealed tuberculous meningitis and brain tuberculomas. The tuberculostatic therapy was reinitiated conjointly with antiepileptic treatment, with favorable clinical outcomes at one year follow-up interval. The imagery findings at one year showed persistent, but reduced tuberculosis lesions.
CONCLUSIONS:
Development of tuberculous meningitis as a paradoxical reaction following appropriate anti-tuberculous therapy in an immunocompetent adult, and is rare and may represent a clinical and radiological challenge. Seizures are commonly associated with brain granulomas and most often resolve after successful medical treatment of the underlying CNS tuberculosis. However, these patients should be kept under observation even after completion of anti-tuberculous treatment. The patient’s compliance and adherence to the treatment along with access to accurate diagnostic procedures play a critical role in the successful long-term tuberculosis management.
Keywords: Epilepsy, Tuberculoma, Intracranial, Tuberculosis





