A Case of Type 2 Diabetes with Hemochromatosis: Efficacy of Changes in Insulin by Switching From Glargine to Degludec
Med Sci Case Rep 2015; 2:72-77
DOI: 10.12659/MSCR.896495
Available online: 2015-12-15
Published: 2015-12-15
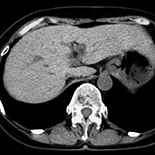
BACKGROUND:
Hemochromatosis is a disease characterized by abnormal iron accumulation in several organs, which may have native or acquired etiologies. Many patients with hemochromatosis have diabetes, which is characterized by insulin deficiency and insulin resistance and is difficult to control.
CASE REPORT:
We report herein on our experience with a 72-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes and hemochromatosis that was difficult to manage. We were able to successfully control the diabetes in this patient by changing the basal insulin analog from glargine to degludec, a new ultra-long-acting agent.
CONCLUSIONS:
A transition in basal insulin from glargine to degludec may reduce the risk of hypoglycemia, lower the total daily insulin dose, and help stabilize blood glucose levels.
Keywords: Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2, Hemochromatosis, Insulin, Long-Acting





